About Orifice Flange
An orifice flange is a specific type of flange used in piping systems for the purpose of measuring the flow rate of fluids. It consists of a pair of flanges with an orifice plate sandwiched between them. The orifice plate has a hole (orifice) drilled through it, which creates a restriction in the flow path. When fluid passes through the orifice, there is a drop in pressure across the plate. This pressure drop is proportional to the flow rate of the fluid, according to the principles of Bernoulli's equation and fluid dynamics.
Orifice flanges are commonly used in industries such as oil and gas, chemical processing, water treatment, and power generation. They are installed in pipelines where accurate measurement and control of fluid flow rates are essential. Orifice flanges are available in different sizes, materials (such as carbon steel, stainless steel, and alloy steel), and pressure ratings to suit various application requirements.
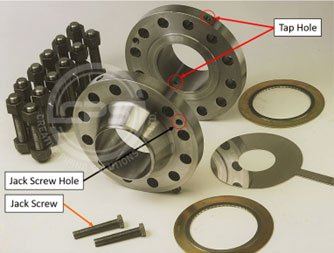
The main components of an orifice flange assembly include:-
Flanges: Orifice flanges consist of two standard flanges (typically ANSI/ASME B16.36) that are used to connect the orifice assembly into the pipeline.
-
Orifice Plate: The orifice plate is a crucial component that sits between the flanges. It contains a precisely engineered hole (orifice) that creates a restriction in the flow path, causing a pressure drop across the plate.
-
Orifice Plate Holders or Restriction Unions: These components secure the orifice plate within the flange assembly and ensure proper alignment and sealing.
-
Gaskets: Gaskets are used to seal the connection between the flanges and the orifice plate assembly, preventing fluid leakage.
-
Bolts and Nuts: Bolts and nuts are used to secure the flanges together, ensuring a tight and leak-free connection.
-
Jack Screws: In some designs, jack screws or studs are used to accurately position and secure the orifice plate within the assembly.

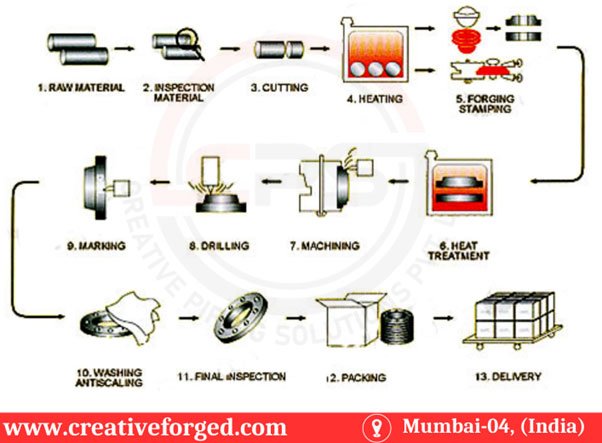
As a premier exporter and distributor, Creative Piping Solutions delivers ANSI/ASME B16.36 Orifice Flanges to markets Including the USA, UAE, Saudi Arabia, Oman, and Qatar.




